How to Choose Cationic Conditioners for Shampoo
The conditioning performance of shampoo has always been a key focus and challenge in shampoo development. In addition to the silicone oil, the choice of cationic ingredients is also important. In this article, we will explore how to choose cationic conditioners in shampoo.
The user experience of shampoo is closely related to the conditioning agents used in the formula. These conditioning agents can reduce the dryness caused by excessive cleaning of hair by surfactants. They intelligently allow an appropriate amount of hydrophobic components to attach to the hair surface, making the hair smoother, preventing tangling, reducing frizz, and also partly adhering to the surface of the hair, repairing the structure of the cuticle.
Common Cationic Conditioners - Classification & Properties
1.Cationic Cellulose
Polyquaternium-10 is prepared by reacting hydroxyethyl cellulose with 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride. Depending on molecular weight and charge density, Polyquaternium-10 has different product variants.
| Ucare Product | Type | Viscosity Grade | % Nitrogen |
| Polymer | JR | 125 | 1.5-2.2 |
| Polymer | JR | 400(SQ-QUAT 400) | 1.5-2.2 |
| Polymer | JR | 30M(SQ-QUAT 3000) | 1.5-2.2 |
| Polymer | LR | 400 | 0.8-1.1 |
| Polymer | LR | 30M | 0.8-1.1 |
| Polymer | LK | -- | 0.4-0.6 |
Polyquaternium-67 is a quaternized hydroxyethyl cellulose, where trimethylamine and lauryl dimethylamine cations replace the original structure. It not only retains the excellent properties of Polyquaternium-10 but also features moderate hydrophobic modification, offering outstanding wet and dry combing performance.
2.Synthetic Polyquaternium Conditioners
There are many types of synthetic polyquaternium conditioners, most of which are homopolymers of cationic monomers or copolymers of cationic monomers with other polymerizable monomers.

1)Polyquaternium-6(SQ-QUAT 6P):PQ6
This is a homopolymer of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, with a molecular weight between 80,000 and 120,000. It has a small molecular weight and high charge density, offering excellent wet and dry combing properties, leaving hair soft and voluminous after drying.
2)Polyquaternium-7 (SQ-QUAT 7P):PQ7
This is a copolymer of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride and acrylamide, with an average molecular weight of about 500,000 and a relatively low charge density. It provides excellent wetting and softening properties for hair, has good foaming and thickening effects, and does not cause buildup, making it widely used in 2-in-1 shampoos.
3)Polyquaternium-11(SQ-QUAT 11P):PQ11
A quaternized copolymer of vinyl pyrrolidone and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, with an average molecular weight of about 1,000,000, forming a transparent, non-sticky continuous film.
4)Polyquaternium-22 (SQ-QUAT 22P):PQ22
A copolymer of acrylic acid and dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, with a molecular weight between 100,000 and 500,000. It provides excellent smoothness and can be used in clear shampoos.
5)Polyquaternium-28 (SQ-QUAT 28P):PQ28
A copolymer of vinyl pyrrolidone and methacrylamide propyl trimethylammonium chloride, which also offers good conditioning effects on hair.
6)Polyquaternium-47 (SQ-QUAT 47P):PQ47
A terpolymer of acrylic acid, methyl acrylate, and methacrylamide propyl trimethylammonium chloride. It has excellent wet combing and anti-tangling properties, typically used at a concentration of 1.5% in shampoos.
Mechanism of Action of Cationic Conditioners – Charge & Flocculation
The mechanism by which cationic conditioners work on hair can be divided into two main types: charge interaction and flocculation.
1.Charge Interaction
Cationic conditioners, which carry a positive charge, are attracted to the negatively charged hair fibers and adsorb onto them. Most water-soluble cationic polymer conditioners attach to the hair in this way, providing excellent conditioning effects for wet hair.
2.Flocculation Mechanism
Flocculation occurs during the dilution process of shampoo. It refers to the interaction between positively charged cationic conditioners and the anionic surfactants in the formula, forming water-insoluble gel complexes. These flocculated gels are difficult to rinse off during the washing process and therefore deposit on the hair. Cationic conditioners deposited through flocculation not only remain effectively on the hair but can also help other ingredients in the shampoo, such as silicones and active substances, to deposit effectively onto the hair.
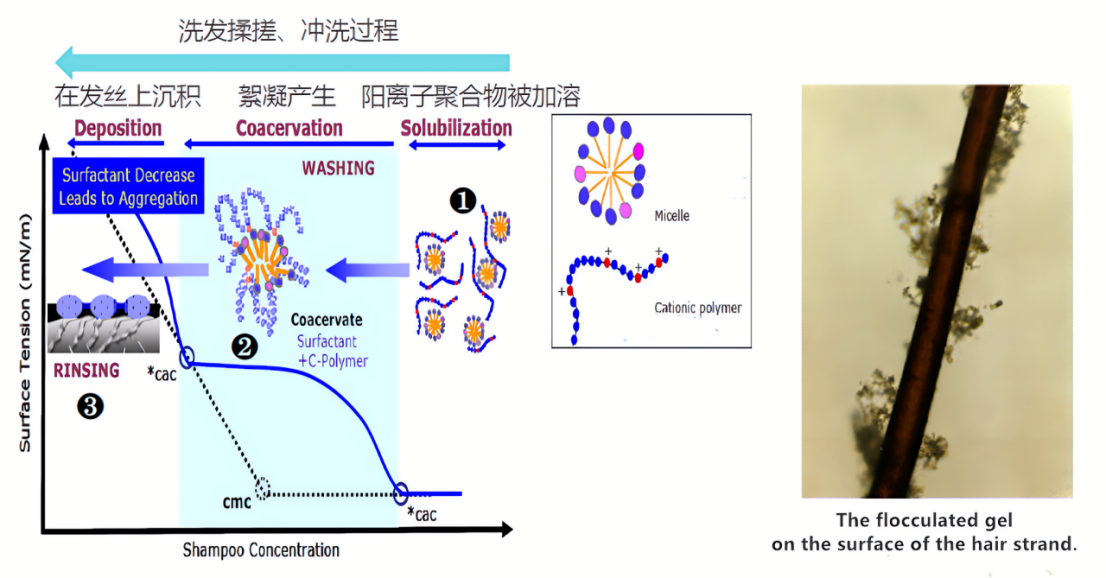
Several factors influence flocculation. Cationic polymers with a high charge density tend to form more flocculent gels, while polymers with a higher molecular weight also generate more flocculent gels. The more flocculent gel present, the better the dry and wet combing performance (slip) of the shampoo.
Cationic Selection – Formula Applications
The main function of cationic hair conditioners in shampoo products is to improve the dry and wet combing properties of the hair, increase softness, provide anti-static effects, and reduce tangling. Different cationic conditioners, due to their structural composition, molecular weight, and charge density, have varying performance characteristics. Moreover, the combination of different conditioners can lead to different conditioning effects. Given the diversity and constant change in market demand, no single cationic conditioner can meet all needs. Therefore, during product development, it is crucial to select the appropriate conditioner for different target audiences and their specific needs.
Common Conditioners Under Specific Conditions
| Feature | PQ7 | PQ22 | PQ28 | PQ6 | PQ73 | PQ10 (JR) | PQ67 | Guar Gum(SQ-Guar 14S) |
| Water Rinse Smoothness | + | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| Durability | + | + | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ |
| Wet Combing | + | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ |
| Wet Softness | + | + | ++++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| Dry Combing | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ |
| Dry Lightness | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | ++ | + | + |
| Dry Softness | + | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| Antistatic | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Aggregation | + | + | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++++ |
It is important to note that even with the same INCI name for cationic conditioners, different models or brands may have variations in molecular weight or charge density, resulting in significant differences in performance. The combination of different conditioners can have a synergistic effect, complementing each other's strengths to achieve conditioning effects that differ from those of a single conditioner.
Commonly Used Conditioner Combinations
| Combination | Conditioning Features |
| 0.25% PQ10 + 0.1% Guar Gum | Medium conditioning. Better durability than PQ10 alone, maintains smoothness post-rinse. Aggregation lower than Guar Gum-based systems. |
| 0.3% Guar Gum + 1% PQ7 | Medium conditioning. Good durability, maintains smoothness post-rinse. Improves softness and volume compared to Guar Gum alone. |
| 0.2% Guar Gum + 0.6% PQ6 (35%) | Heavy conditioning. Smooth and silky feel, suitable for fine and easily broken hair. |
| 0.07% PQ10 + 0.08% Guar Gum + 0.3% PQ6 + 0.5% PQ22 (40%) | Medium conditioning. Smooth post-rinse, wet combing smooth, dry hair silky. Good volume, low aggregation, no noticeable change with repeated use. |
| 1% PQ6 (35%) + 0.7% PQ22 (40%) | Light conditioning. Smooth and silky post-rinse, suitable for light conditioning and volume products. |
| 0.1% Guar Gum + 1% PQ6 (35%) + 0.4% PQ22 (40%) | Medium to high conditioning. Smooth and silky, good durability. Good repair and color protection, maintains volume. Suitable for color and perm products. |
| 2% PQ6 (35%) + 0.6% PQ22 (40%) (Transparent System) | High conditioning. Smooth and silky, good repair. Soft and voluminous dry hair, good color protection. Suitable for repair products. |



